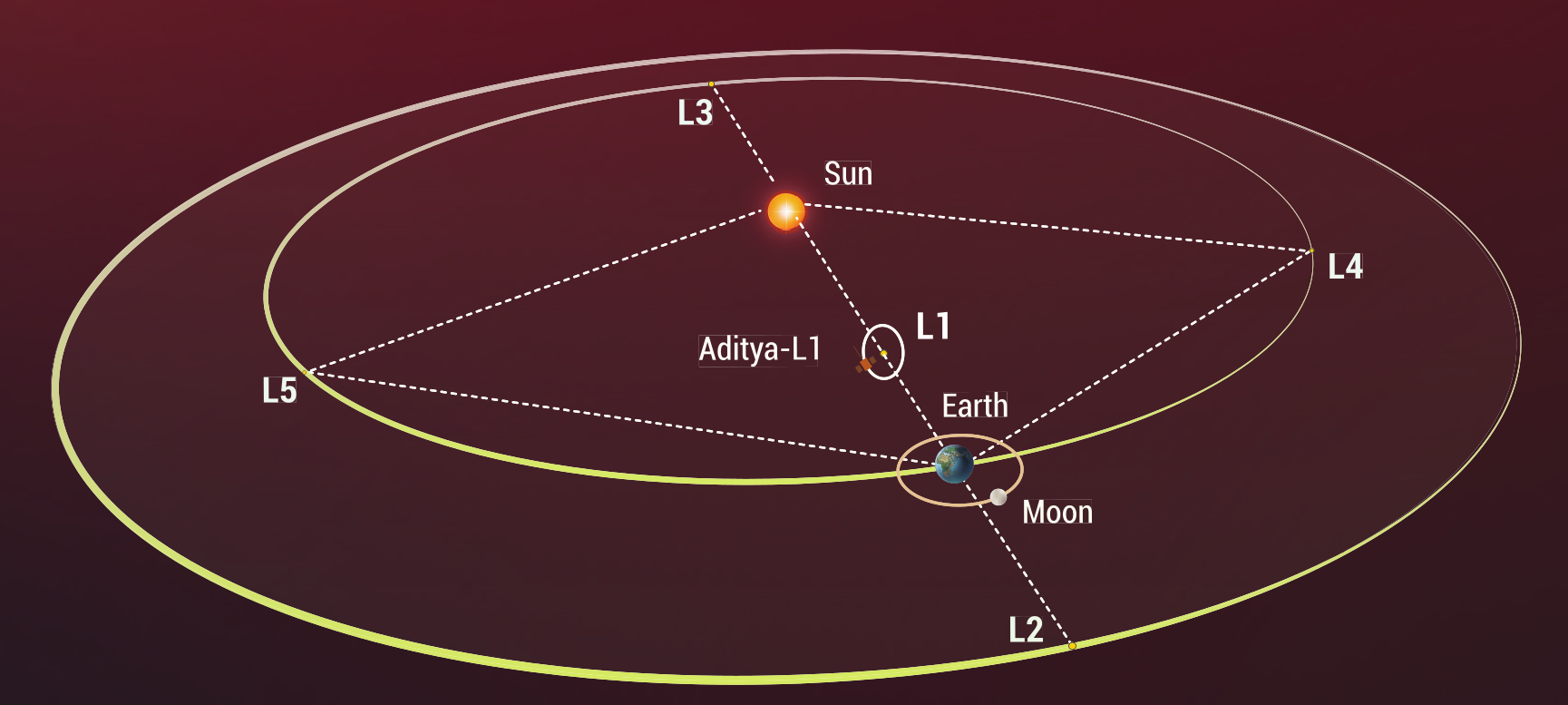
Aditya-L1 is ISRO’s first solar mission dedicated to solar observations. The satellite is placed in a halo orbit around the first Lagrangian Point (L1), located 1.5 million km from Earth on the line connecting the Sun and Earth. This unique location enables uninterrupted observations of the Sun.
The spacecraft carries seven payloads, four for remote sensing and the remaining three for in-situ measurements. Together, these seven payloads will enable the multi-wavelength study of the dynamics of the Sun and its impact on the near-earth environment. The details of the payloads are given below.
Remote sensing payloads
1. Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT)
2. Visible Imaging Line Coronagraph (VELC)
3. SOlar Low Energy Spectrometer (SoLEXS)
4. High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray Spectrometer (HELIOS)
Payloads for in-situ measurements
1. Aditya Solar Wind Particle EXperiment (ASPEX)
2. Plasma Analyser Package for Aditya (PAPA)
3. Magnetometer (MAG)
What does Aditya-L1 mean?
In Hindu mythology, the Adityas were the 12 children of the goddess of infinity- Aditi. In present-day Sanskrit, Aditya is synonymous with Surya, the Sun, and the twelve Adityas are believed to represent the twelve months of a year. L1 refers to the Sun-Earth Lagrange 1 point where Aditya is housed.
What is Lagrange 1?
Lagrange points are locations in space produced by two massive bodies where small objects tend to stay at rest when placed. A total of five such Lagrange points exist, among which L1 lies at a distance of 1.5 million km, from the Earth- 1% closer in the direction of the Sun.
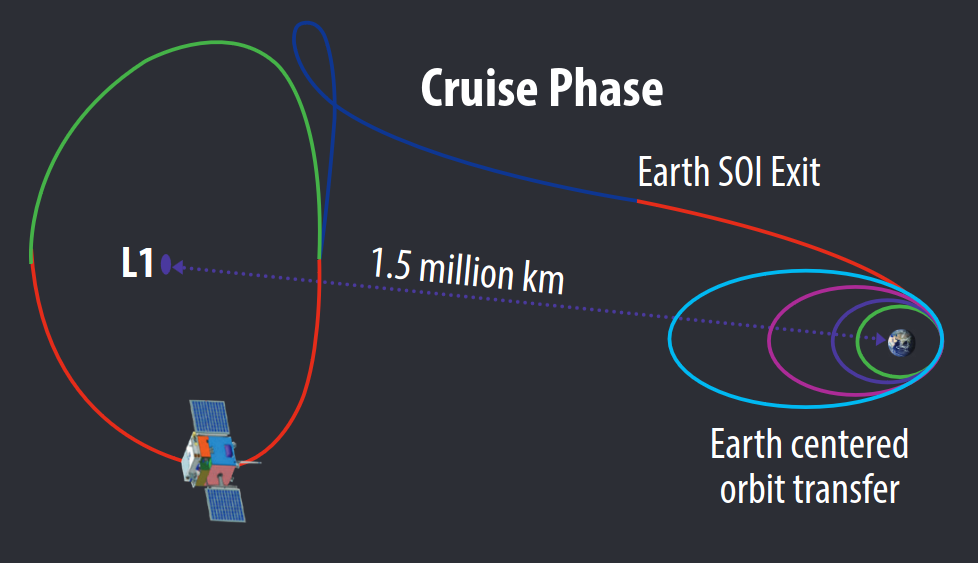
What was the flight plan to L1?
Aditya-L1 was launched by ISRO's PSLV-XL from Satish Dhawan Space Center SHAR (SDSC-SHAR), Sriharikota, India on Sep 2, 2023. Initially, the spacecraft was placed in a Low Earth Orbit, which was subsequently made more elliptical and was slingshot towards the Lagrange 1 point using the spacecraft propulsion module. After a cruise of about four months, the satellite reached the L1 position, where it was injected into a halo orbit around the L1 point, which it revolves once every six months.